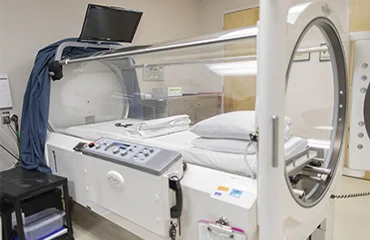
HBOT stands for Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. It is a medical treatment that involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber. The increased pressure allows the body to absorb more oxygen than it would at normal atmospheric pressure, which can have a variety of therapeutic benefits.
It has been used to treat a wide range of medical conditions, including decompression sickness, carbon monoxide poisoning, non-healing wounds, radiation injury, and more. It has also been used in sports medicine to aid in recovery from injuries.