Diabetic foot infections are a common and serious complication of diabetes that can lead to severe medical complications if left untreated. People with diabetes are more prone to foot infections due to nerve damage, poor circulation, and weakened immune systems. Foot infections can range from mild to severe and can be caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses.
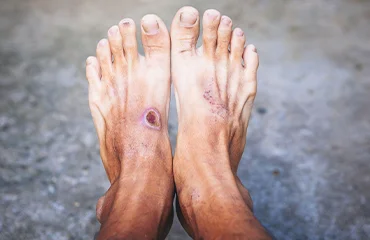
What are diabetic foot infections?
Here are some common types of diabetic foot infections:
1. Cellulitis: This is a bacterial infection of the skin and underlying tissues that can cause redness, swelling, warmth, and pain.
2. Osteomyelitis: This is a bone infection that can occur when bacteria enter the bone through a wound or ulcer. It can cause severe pain, swelling, and fever.
3. Necrotizing fasciitis: This is a rare but serious bacterial infection that affects the soft tissues of the foot. It can cause tissue death and may require surgery to remove the infected tissue.
4. Fungal infections: Diabetes can increase the risk of fungal infections such as athlete's foot, which can lead to further complications if left untreated.
Diabetic foot infections can lead to serious complications such as foot ulcers, gangrene, and even amputation. Treatment for diabetic foot infections depends on the severity and type of infection. Mild infections may be treated with antibiotics, wound care, and off-loading (reducing pressure on the foot). More severe infections may require hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics.
Preventing diabetic foot infections is key. People with diabetes should inspect their feet daily for cuts, blisters, and other injuries. They should also wear comfortable shoes that fit properly and avoid walking barefoot. Keeping blood sugar levels under control can also reduce the risk of foot infections. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify and manage foot-related complications before they become serious.
