endoscopy
About endoscopy
Endoscopy Services at Nano Hospitals provide minimally invasive procedures that allow doctors to view, diagnose, and sometimes treat conditions inside the digestive tract and other internal organs without major surgery. Using advanced endoscopic technology, specialists can examine internal structures with high clarity, enabling early detection of disease and precise medical intervention.
These procedures play a vital role in identifying gastrointestinal disorders, bleeding, ulcers, polyps, tumors, and chronic digestive problems while ensuring patient comfort and faster recovery.
Overview
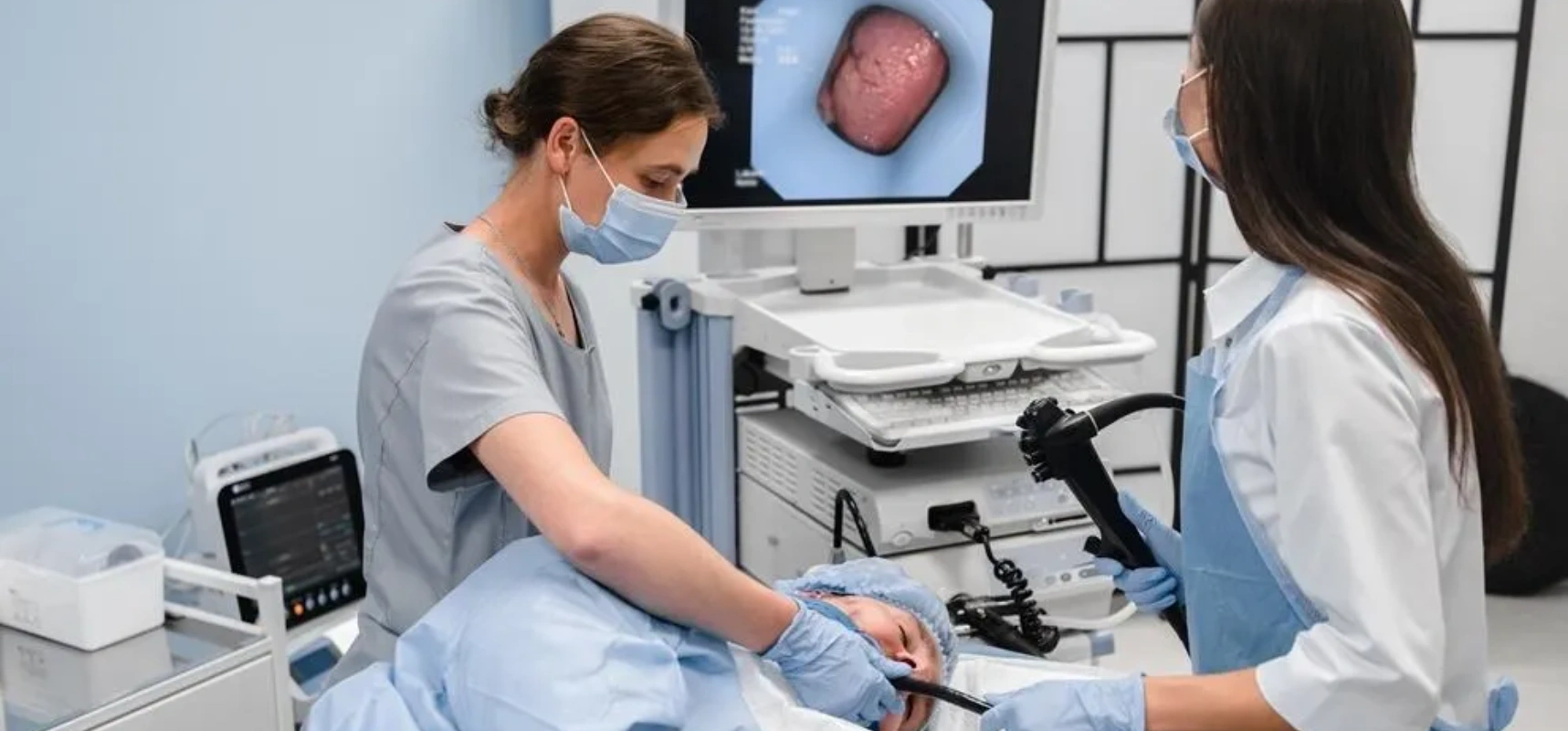
Endoscopy is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure that uses a flexible tube with a light and camera (endoscope) to examine the inside of the body. It is most commonly used to assess the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and colon, but may also be used for airways, urinary tract, or other internal structures depending on the medical need.
At Nano Hospitals, Endoscopy Services are performed by trained specialists using high-definition imaging systems and modern equipment to ensure accurate diagnosis and safe intervention.
Workflow
Step 1: Medical Evaluation
The doctor evaluates symptoms such as abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing, chronic acidity, bleeding, or unexplained weight loss and recommends an endoscopic examination.
Step 2: Preparation
Patients receive instructions such as fasting or bowel preparation (for colonoscopy) to ensure clear visibility during the procedure.
Step 3: Sedation and Monitoring
Mild sedation or local anesthesia may be given for comfort. Vital signs are monitored throughout.
Step 4: Endoscopic Examination
The endoscope is gently inserted through the mouth or rectum (depending on the procedure) to view internal organs in real time.
Step 5: Biopsy or Treatment (If Needed)
Doctors can take tissue samples, stop bleeding, remove polyps, or perform minor therapeutic procedures during the same session.
Step 6: Recovery and Reporting
After the procedure, patients are observed briefly and then discharged with findings and follow-up advice.
Benefits & Value
For Patients
Early detection of ulcers, inflammation, tumors, and polyps
Minimally invasive diagnosis without major surgery
Faster recovery and shorter hospital stays
For Doctors
Direct visualization of internal organs for accurate diagnosis
Ability to perform biopsy and minor treatments immediately
Better monitoring of chronic gastrointestinal diseases
For the Community
Improved early detection of digestive cancers
Reduced need for open surgical diagnostic procedures
Access to advanced digestive healthcare locally
Risks & Challenges
- • Mild throat discomfort or abdominal bloating after procedure
- • Small risk of bleeding, infection, or perforation
- • Sedation-related side effects in sensitive individuals
- • Need for proper patient preparation for accurate results
